Host isolation allows you to isolate hosts from your network, blocking communication with other hosts on your network until the host is released. Isolating a host helps respond to malicious activity or prevent potential attacks, as it prevents lateral movement across other hosts. However, isolated hosts can still send data to Elasticsearch and Kibana.
For Elastic Stack version >= 7.15.0, host isolation is supported for endpoints running Windows, macOS, and these Linux distributions:
CentOS/RHEL 8
Ubuntu 18.04
Ubuntu 20.04
AWS Linux 2
Login to Elastic Endpoint Security. Please refer to How to access Elastic Endpoint Security if you need assistance with this.
Once you're logged into the system, navigate to Security → Manage → Endpoints.
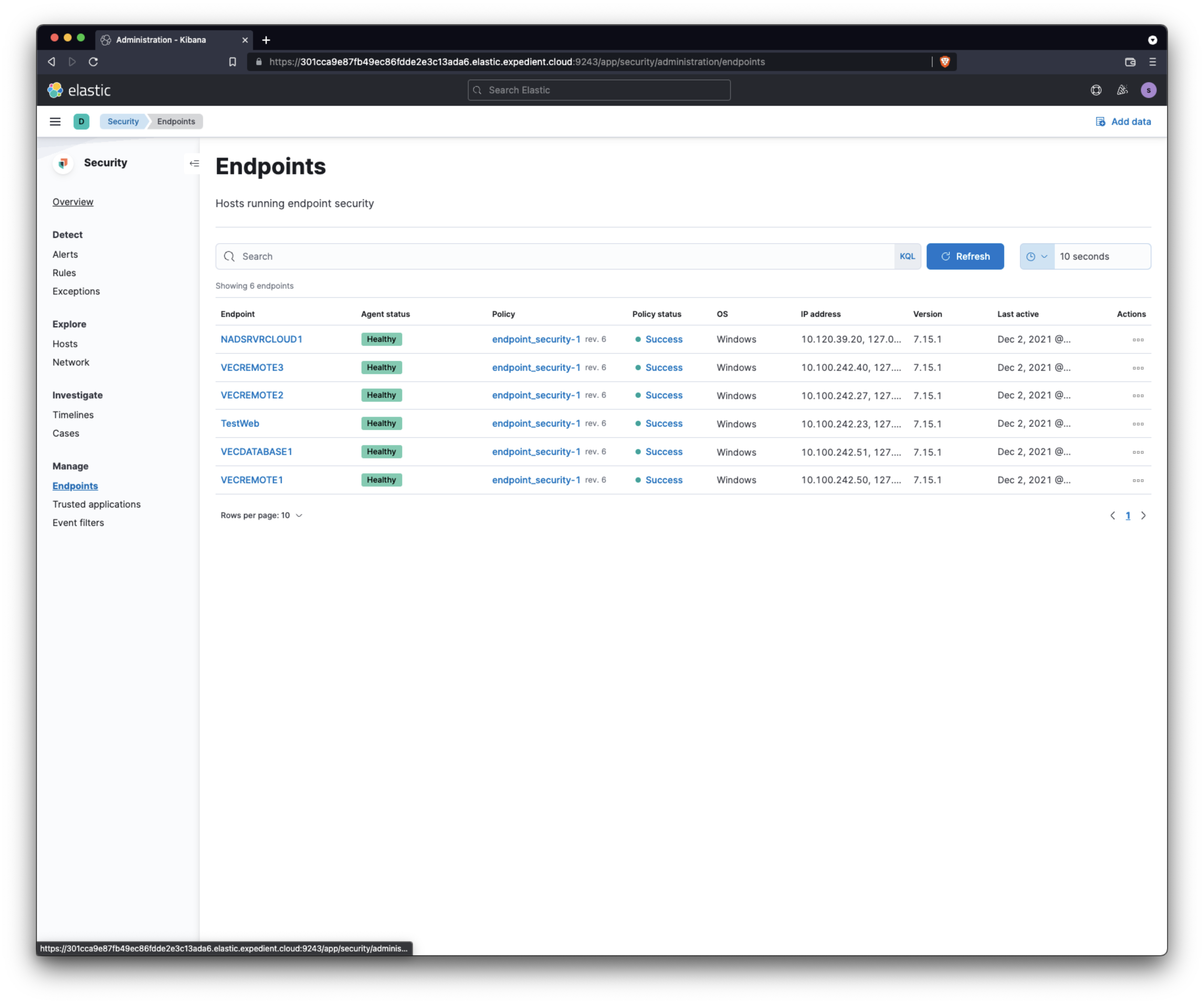
Enter the name of the machine you want to isolate in the search box, hit enter, then click the endpoint name.
In the right-hand corner of the next window, click Take Action, then click click Isolate host.
Warning
Clicking the Isolate host button will cause the machine to go offline and is Service Impacting. Do not perform this action unless you are sure the system is supposed to be offline.
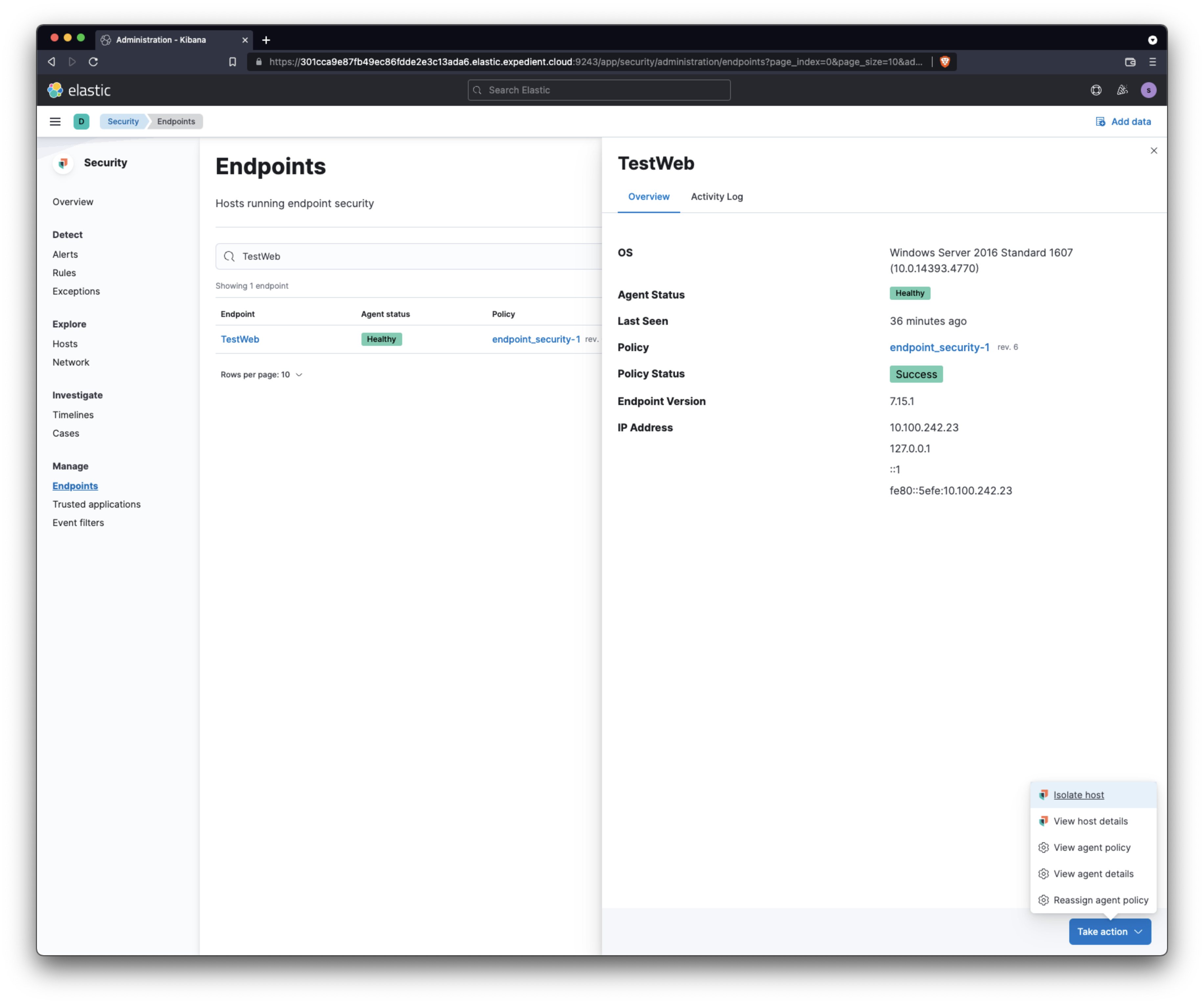
The machine will go offline, and you'll need access to the console to manage it. If you need to remove the isolation, perform steps 3 and 4 and click Release Host.